Sorry for the delay in postings, but many of us are in the state of transition, whether its school, weddings or work. As a simple tutorial to get back into the swing of things, let’s look at several different ways of requesting user input in your MATLAB programs. While you will often need to display information to the user, you will have to request data from them as well. There are several options available to you, and we will run through many of them here. The most basic of which is the command line based “input”.
Tag Archives: matlab
Managing Your Path in Matlab – Part II
In the last article I wrote about managing your path in Matlab, I covered some of the functions that deal with the search path, including path, matlabroot, addpath, rmpath and genpath. These functions provide a solid base for viewing, adding and removing directories from your search path. In this article, I will explain how to use several more functions that deal with your search path, including functions that make changes which persist after ending your Matlab session. Continue reading
Modeling with ODEs in Matlab – Part 3
Well, I feel like I should apologize for such a long delay between posts. It’s been a crazy summer that has included some vacation time plus an overseas trip to a conference. Regardless, I’m finally back in the swing of things and ready to write up Part 3! To recap: Lesson 1 and Lesson 2 looked at how ODEs are solved numerically and how higher order solutions are more accurate than naive implementations. Today we’ll look at two simulations of living systems (Lotka-Volterra and SIR). Finally, the series will conclude with a post on model fitting and a post about chaotic systems.
Continue reading
Clustering Part 2: K-means clustering
Clustering data is the act of partitioning observations into groups, or clusters, such that each data point in the subset shares similar characteristics to its corresponding members. Cluster analysis is commonly used in fields that utilize data mining, pattern recognition and machine learning. While MATLAB has several clustering tools included in its arsenal, we’ll take a look at the function kmeans in this tutorial. Following classification of n observations into k clusters, we can use binary classification to investigate the sensitivity and specificity of our clustering.
Managing Your Search Path in Matlab – Part I
Management of your search path in Matlab is an important skill that every Matlab programmer should have. Your search path is the ordered set of directories that Matlab uses to find a function that you call. Being aware of your search path is a good habit, especially if you are working with multiple versions of the same code. In this post and the following post, I will describe how to use Matlab to modify your search path. Continue reading
Clustering Part 1 – Binary Classification
Binary classification is the act of discriminating an item into one of two groups based on specified measures or variables. While previously we have discussed methods for determining values of logic gates using neural networks (Part 1 and Part 2), we will begin a series on clustering algorithms that can be performed in Matlab, including the use of k-means clustering and Gaussian Mixture Models. Prior to doing so, we will discuss how classification is evaluated, primarily through the discussion of sensitivity, specificity and the way to calculate these values through Matlab.
Neural Networks – A Multilayer Perceptron in Matlab
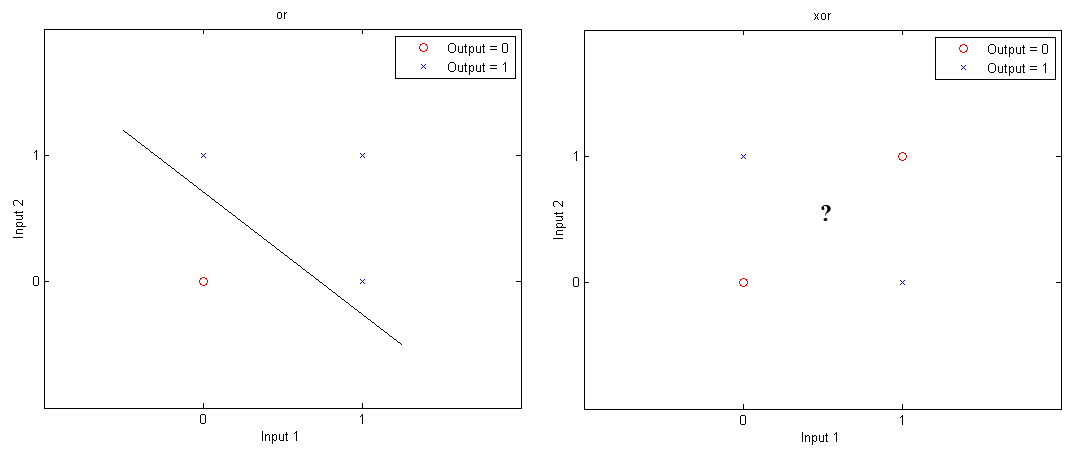
Previously, Matlab Geeks discussed a simple perceptron, which involves feed-forward learning based on two layers: inputs and outputs. Today we’re going to add a little more complexity by including a third layer, or a hidden layer into the network. A reason for doing so is based on the concept of linear separability. While logic gates like “OR”, “AND” or “NAND” can have 0’s and 1’s separated by a single line (or hyperplane in multiple dimensions), this linear separation is not possible for “XOR” (exclusive OR).
Modeling with ODEs in Matlab – Part 2
Hello again! Today I’m back with Lesson 2 of our ongoing five part series on ODE modeling. Previously, Lesson 1 introduced the use of ODEs as a method of modeling population dynamics and discussed a simple method of evaluating the equations. Today, we will look at Matlab’s implementation of the Runge-Kutta method for solving ODEs. Lesson 3 will explore techniques for designing more realistic models. Lesson 4 will discuss methods for matching these abstract models to empirical data. Finally, we will play around with some fun ‘chaotic’ systems in Lesson 5.
Continue reading